Understanding and Managing Skin Rashes in Children: A Simple Guide for Parents
Children often experience skin rashes, a common concern that can be worrisome for parents. Skin rashes in children can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from allergies to infections. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of skin rashes in children, common causes, preventive measures, and when to seek medical attention.
What are Skin Rashes?
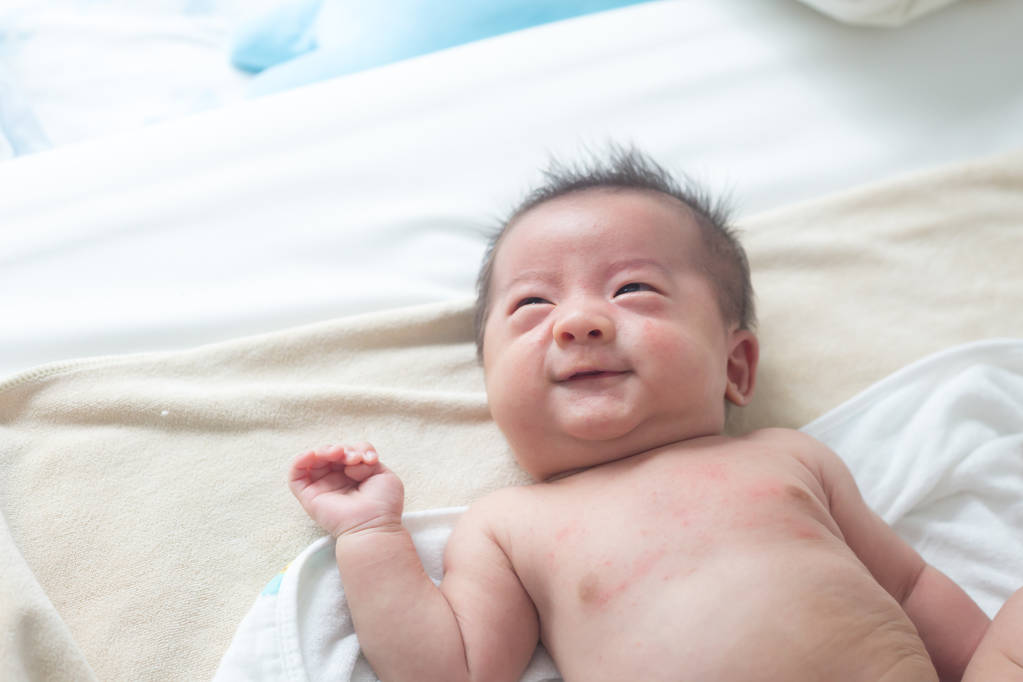
A skin rash is a noticeable change in the texture or color of the skin. Rashes can be characterized by redness, itching, and the presence of small bumps or blisters. In children, skin rashes are particularly common due to their sensitive skin and exposure to various environmental factors.
Common Causes of Skin Rashes in Children:
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema is a chronic condition that often begins in infancy. It results in dry, itchy skin, and rashes can appear on different parts of the body. Common triggers include certain foods, allergens, and environmental factors.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type of rash occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Common culprits include certain soaps, lotions, fabrics, or even plants like poison ivy.
- Heat Rash: Also known as prickly heat, heat rash occurs when sweat gets trapped in sweat ducts, leading to red, itchy bumps. This is more common in hot and humid weather.
- Viral Infections: Many viral infections, such as chickenpox, measles, or hand, foot, and mouth disease, can cause characteristic rashes. These rashes are often accompanied by other symptoms like fever.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections, like impetigo, can lead to red sores or blisters on the skin. These are usually contagious and may require medical attention.
- Allergies: Children can be allergic to various substances, including certain foods, insect bites, or medications, which can result in skin rashes.
- Insect Bites: Mosquito bites, bee stings, or bites from other insects can cause localized redness, swelling, and itching.
- Fungal Infections: Fungi, such as ringworm or yeast, can cause skin infections leading to rashes. These infections are typically treatable with antifungal medications.
Identifying the Rash:
Understanding the characteristics of a rash can provide valuable information about its cause. Here are some common types of rashes and their features:
- Eczema Rash: Eczema rashes are often red, dry, and itchy. In severe cases, the skin may crack or bleed. The rash can appear on the face, elbows, knees, and other areas.
- Contact Dermatitis: This rash is usually red, itchy, and may have blisters. It appears on the area of skin that came into contact with the irritant or allergen.
- Heat Rash: Heat rash consists of small, red bumps that can be itchy. It often occurs in areas where sweat is trapped, such as the neck, armpits, or groin.
- Viral Rashes: Viral rashes vary depending on the virus but can include red spots, raised bumps, or a more generalized redness. The appearance may change as the infection progresses.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections like impetigo present as red sores or blisters that may ooze and form a crust. They are often located around the mouth or nose.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic rashes can vary widely in appearance, from hives (raised, red welts) to a more diffuse redness.
Preventive Measures for Skin Rashes:
While some rashes are unavoidable, certain measures can help prevent or minimize the occurrence of skin rashes in children:
- Use Mild Soaps and Detergents: Opt for gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents to avoid irritating your child’s skin.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin well-hydrated can prevent dryness and reduce the likelihood of eczema flare-ups.
- Avoid Allergens: Identify and eliminate potential allergens from your child’s environment, including certain foods, plants, or fabrics.
- Dress Appropriately: Choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing for your child, especially in hot weather, to prevent heat rash.
- Insect Protection: Use insect repellent to protect your child from insect bites, and dress them in long sleeves and pants in areas where insects are prevalent.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Encourage regular handwashing to reduce the risk of bacterial and viral infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
While many rashes can be managed at home, some may require medical attention. Parents should seek medical advice if:
- The rash is spreading rapidly or getting worse.
- Your child has a fever along with the rash.
- The rash is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face.
- Your child seems unwell or is unusually irritable.
Treatment of Skin Rashes:
The treatment of a skin rash depends on its cause. In general, the following measures can be helpful:
- Topical Creams or Ointments: For rashes caused by eczema or contact dermatitis, your healthcare provider may prescribe or recommend over-the-counter creams to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: These medications can help relieve itching associated with allergic reactions.
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses can provide relief for rashes associated with heat or irritation.
- Antifungal Medications: If the rash is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal creams or medications may be prescribed.
- Antibiotics: Bacterial infections may require antibiotics to clear the infection.
Conclusion:
Skin rashes in children are a common and usually benign occurrence. While they can be concerning for parents, understanding the causes, identifying the type of rash, and implementing preventive measures can go a long way in managing and preventing them. If in doubt, consulting with a healthcare professional ensures proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, providing your child with the best care for their skin health.